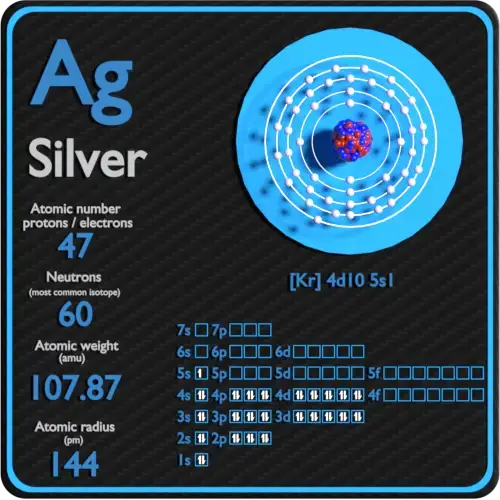
Silver is a soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of whatever metal. The metallic is found in the Earth's chaff in the pure, complimentary elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, aureate, pb, and zinc refining.
Protons and Neutrons in Silver
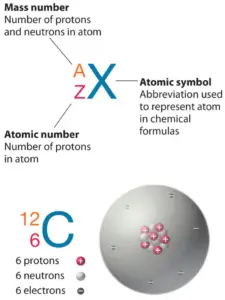 Silver is a chemic element with atomic number47 which ways there are 47 protons in its nucleus. Full number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where east (unproblematic charge) equals toane,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Silver is a chemic element with atomic number47 which ways there are 47 protons in its nucleus. Full number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where east (unproblematic charge) equals toane,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
The full number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is chosen theneutron number of the atom and is given thesymbol North. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number:N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as theneutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
For stable elements, at that place is ordinarily a variety of stable isotopes. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the aforementioned element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Silvery are107, 109.
Main Isotopes of Silver
Silver occurs in 2 natural isotopes: 107Ag and 109Ag.107Ag is the most mutual isotope, having a natural abundance of approximately 51%.
Silver-107 is composed of 47 protons, threescore neutrons, and 47 electrons.
Argent-109 is equanimous of 47 protons, 62 neutrons, and 47 electrons.
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the aforementioned as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral cantlet of Silverish is 47. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – one) negative electrons in the atom.
Since the number of electrons and their organisation are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, thediminutive number identifies the various chemical elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element's electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the chief gene in determining its chemic bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing diminutive number Z.
Electron configuration ofSilveris[Kr] 4d10 5s1.
Possible oxidation states are+i.
Most Mutual Awarding of Silver
Silvery has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metallic is used in many bullion coins, sometimes alongside gold. Argent has many important, far-reaching technological and electronic applications. It's used in everything from prison cell phones, computers and semiconductors to automobiles, water-purification systems and—considering it is the all-time conductor of heat of all elements—spacecraft solar radiations tiles.
About Protons
 A proton is 1 of the subatomic particles that brand up matter. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upabout one-half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a remainder mass equal to one.67262 × 10−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron simply nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 × 10−15 thousand, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
A proton is 1 of the subatomic particles that brand up matter. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upabout one-half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a remainder mass equal to one.67262 × 10−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron simply nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 × 10−15 thousand, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
The protons be in the nuclei of typical atoms, along with their neutral counterparts, the neutrons. Neutrons and protons, normally chosennucleons, are jump together in the atomic nucleus, where they account for 99.9 percent of the atom'south mass. Inquiry in loftier-free energy particle physics in the 20th century revealed that neither the neutron nor the protonis not the smallest edifice cake of matter.
About Neutrons
A neutron is one of the subatomic particles that make up matter. In the universe, neutrons are abundant, making upmore than half of all visible matter. It hasno electric charge and a rest mass equal to ane.67493 × 10−27 kg—marginally greater than that of the proton but nigh 1839 times greater than that of the electron. The neutron has a hateful foursquare radius of about 0.viii×10−15 m, or 0.8 fm, and it is a spin-½ fermion.
Atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons, which concenter each other throughthe nuclear force, while protons repel each other viathe electric strength due to their positive accuse. These two forces compete, leading to various stability of nuclei. There are only certain combinations of neutrons and protons, which formsstable nuclei.
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus, considering they attract each other and protons , which helps showtime the electrical repulsion between protons. As a result, equally the number of protons increases,an increasing ratio of neutrons to protons is needed to form a stable nucleus. If there are too many or also few neutrons for a given number of protons, the resulting nucleus is non stable and it undergoes radioactivity.Unstable isotopesdecay through diverse radioactivity pathways, most commonly alpha decay, beta decay, or electron capture. Many other rare types of decay, such as spontaneous fission or neutron emission are known. Information technology should exist noted that all of these decay pathways may be accompanied pastthe subsequent emission of gamma radiation. Pure alpha or beta decays are very rare.
Most Electrons and Electron Configuration
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemic elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemic properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in diminutive or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of theelectron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Thechemic properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, past number andarrangement of electrons. Theconfiguration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element's electron shells, specially the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding beliefs. In the periodic tabular array, the elements are listed in social club of increasing atomic number Z.
It is thePauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an atom to occupy dissimilar free energy levels instead of them all condensing in the basis state. The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the everyman free energy country (ground state) and moves progressively from there up the energy scale until each of the atom'southward electrons has been assigned a unique gear up of quantum numbers. This fact has central implications for the edifice up of the periodic table of elements.
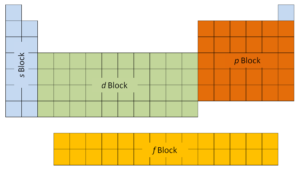 The first ii columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thes subshells are beingness occupied. Because of this, the first ii rows of the periodic table are labeled thes block. Similarly, thep cakeare the right-most six columns of the periodic tabular array, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef cakeis the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the primary body of the periodic table. Information technology could be part of the chief trunk, merely so the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
The first ii columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thes subshells are beingness occupied. Because of this, the first ii rows of the periodic table are labeled thes block. Similarly, thep cakeare the right-most six columns of the periodic tabular array, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef cakeis the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the primary body of the periodic table. Information technology could be part of the chief trunk, merely so the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
For atoms with many electrons, this annotation tin can become lengthy and and then an abbreviated notation is used. The electron configuration can exist visualized equally the core electrons, equivalent to thenoble gas of the preceding menses, and the valence electrons (e.yard. [Xe] 6s2 for barium).
Oxidation States
Oxidation states are typically represented past integers which may be positive, null, or negative. Almost elements take more than one possible oxidation state. For example, carbon has ix possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4.
The current IUPAC Gold Volume definition of oxidation state is:
"Oxidation country of an atom is the accuse of this atom after ionic approximation of its heteronuclear bonds…"
and the term oxidation number is almost synonymous. An element that is not combined with any other different elements has an oxidation state of 0. Oxidation state 0 occurs for all elements – it is simply the element in its elemental grade. An atom of an chemical element in a compound will have a positive oxidation state if it has had electrons removed. Similarly, adding electrons results in a negative oxidation country. We have also distinguish between the possible and mutual oxidation states of every chemical element. For instance, silicon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −iv to +4, simply just -4, 0 and +iv are common oxidation states.
Summary
| Element | Silver |
| Number of protons | 47 |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) | 107, 109 |
| Number of electrons | 47 |
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s1 |
| Oxidation states | +1 |

Source: world wide web.luciteria.com
Other backdrop of Silver

 Silver is a chemic element with atomic number47 which ways there are 47 protons in its nucleus. Full number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where east (unproblematic charge) equals toane,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Silver is a chemic element with atomic number47 which ways there are 47 protons in its nucleus. Full number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where east (unproblematic charge) equals toane,602 x 10-19 coulombs.

 A proton is 1 of the subatomic particles that brand up matter. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upabout one-half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a remainder mass equal to one.67262 × 10−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron simply nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 × 10−15 thousand, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
A proton is 1 of the subatomic particles that brand up matter. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upabout one-half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a remainder mass equal to one.67262 × 10−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron simply nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 × 10−15 thousand, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion. The first ii columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thes subshells are beingness occupied. Because of this, the first ii rows of the periodic table are labeled thes block. Similarly, thep cakeare the right-most six columns of the periodic tabular array, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef cakeis the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the primary body of the periodic table. Information technology could be part of the chief trunk, merely so the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
The first ii columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thes subshells are beingness occupied. Because of this, the first ii rows of the periodic table are labeled thes block. Similarly, thep cakeare the right-most six columns of the periodic tabular array, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef cakeis the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the primary body of the periodic table. Information technology could be part of the chief trunk, merely so the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
0 Response to "Number Of Electrons In Silver"
Post a Comment